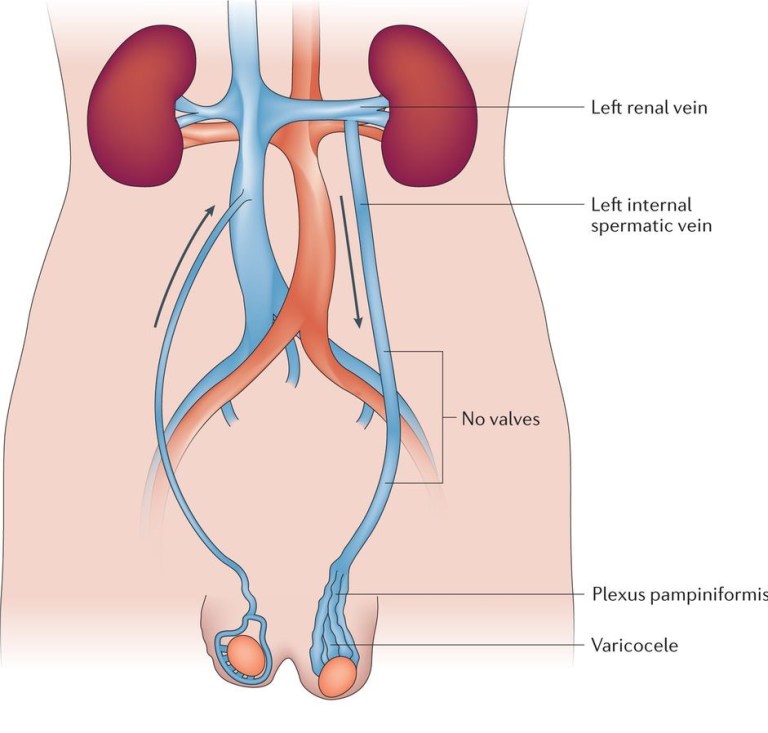
Understanding Varicocele and Its Impact
Varicocele is a condition characterized by the enlargement of veins within the scrotum, similar to varicose veins in the legs. It can lead to discomfort, testicular atrophy, and even infertility in some cases. Affecting nearly 15% of men, varicocele is a common issue, often detected during puberty and progressing over time.
What Is Varicocele Embolisation?
Varicocele embolisation is a minimally invasive procedure designed to treat varicoceles without the need for surgery. Unlike traditional varicocelectomy, which requires an incision, embolisation is performed using a catheter inserted through a small incision in the groin or neck. This method effectively blocks the affected veins, preventing blood from pooling and reducing symptoms.
How Does Varicocele Embolisation Work?
The procedure involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The patient is given local anesthesia and mild sedation to ensure comfort.
- Catheter Insertion: A thin catheter is guided through a small incision into the affected vein using X-ray imaging.
- Blocking the Vein: A special embolic agent, such as coils or a sclerosing solution, is used to block blood flow to the varicocele.
- Closure and Recovery: The catheter is removed, and the small puncture site is covered. No stitches are required.
Benefits of Varicocele Embolisation
1. Minimally Invasive
Unlike open surgery, embolisation requires only a tiny incision, reducing the risk of complications and scarring.
2. Short Recovery Time
Most patients can resume normal activities within 24–48 hours, whereas traditional surgery requires a longer healing period.
3. Less Pain and Discomfort
Since there are no surgical incisions, pain is significantly lower compared to varicocelectomy.
4. High Success Rate
Studies show that varicocele embolisation has a success rate of over 90%, making it an effective treatment option.
5. No Need for General Anesthesia
Patients remain awake during the procedure, avoiding risks associated with general anesthesia.
Who Should Consider Varicocele Embolisation?
This procedure is ideal for individuals who:
- Experience pain or discomfort due to varicocele.
- Have fertility issues linked to varicocele.
- Prefer a non-surgical treatment option.
- Have had unsuccessful varicocelectomy in the past.
Recovery and Aftercare
Following the procedure, patients can expect:
- Mild Discomfort: Some minor pain or swelling may occur but usually subsides within a few days.
- Quick Return to Routine: Most patients resume daily activities within two days, though heavy lifting should be avoided for about a week.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups ensure proper healing and assess improvements in symptoms.
Comparing Varicocele Embolisation and Surgery
| Feature | Varicocele Embolisation | Surgery (Varicocelectomy) |
|---|---|---|
| Invasiveness | Minimally invasive | Requires incisions |
| Recovery Time | 1–2 days | 2–3 weeks |
| Anesthesia | Local anesthesia | General anesthesia |
| Pain Level | Mild discomfort | Moderate to severe pain |
| Success Rate | 90%+ | 85–90% |
Risks and Complications
Though rare, varicocele embolisation may have minor risks such as:
- Bruising or Swelling: Temporary at the insertion site.
- Allergic Reactions: Rare reactions to the contrast dye used in imaging.
- Recurrence: In rare cases, varicoceles may return, requiring further treatment.
Choosing the Right Specialist
Selecting an experienced interventional radiologist is crucial for the success of the procedure. A specialist with expertise in embolisation ensures minimal risks and optimal results.
Conclusion
Varicocele embolisation is an effective, minimally invasive alternative to surgery for treating varicoceles. With a high success rate, quick recovery, and minimal discomfort, it is an excellent option for individuals seeking relief from varicocele-related issues. Consulting a specialist can help determine if embolisation is the right choice for your condition.